Functional programming has become a topic of great interest to the javascript community. Developers want to build more predictable applications by composing functions and assembling components where each piece has its own responsibility. It’s the ultimate modular paradigm.
When it comes to building software, be it a website, a mobile application, or any type of computer software, one of the most noticeable problems is the difficulty to comprehend large projects with complex codebases, often involving dozens of programmers. As a developer, it is common to spend more time figuring out what the code does rather than actually writing code.
One way to avoid poor-planning headaches is to structure your codebase around the concept of modules, each with its own responsibility. The approach is simple and not new, it consists in breaking down your application into smaller, single-purpose business function. It is, in my own opinion, the best solution to building more maintainable javascript applications.
What is a modular structure?
In recent years, fast-growing tech companies witnessed difficulties with traditional organization based functional divisions (e.g marketing, design, development, etc.). Teams were unable to adapt such a fast-changing environment. Spotify was among the first to start organizing its teams into cross-functional tribes — autonomous entities responsible for managing and delivering their own products. Think of it like multiple small companies as part of a larger one. When a tribe becomes too big, it divides itself into new ones and so do the responsibilities. A key reason why companies started exploring this scheme is scalability, as they grow, they need to expand painlessly. If you are not familiar with this concept, I suggest you watch this great video about how Spotify organizes itself.
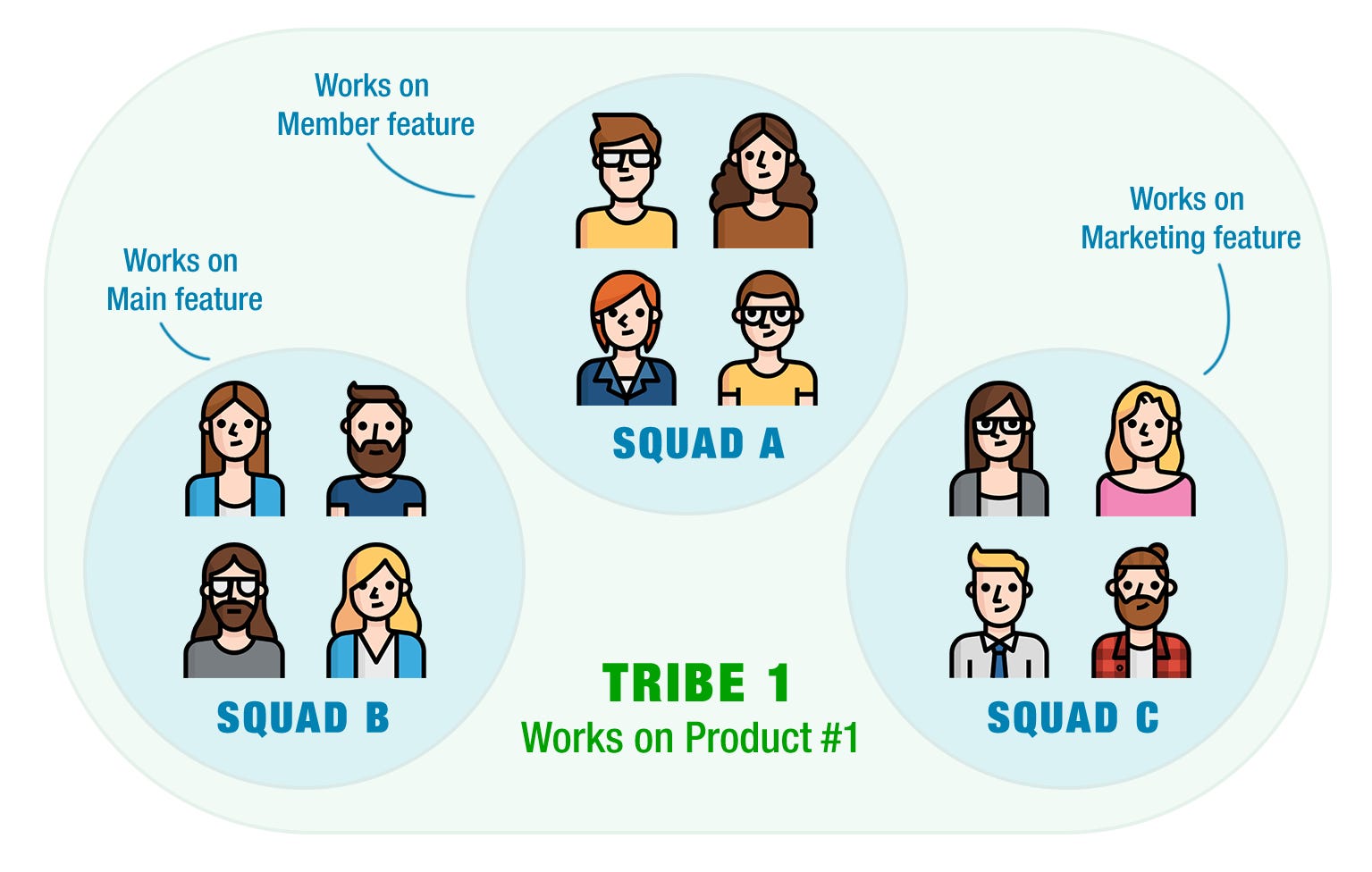
What if the same pattern gets applied to programming?
In programming the same rule can apply. An application is like a tribe and modules are the squads composing it, each having a single responsibility. A module encapsulates a set of related functions and components semantically related with its own functional responsibility. They have all the assets they need to work on their own and can be tested independently of the rest of the application.
Determining a single responsibility suggests a module should never have more than one reason to change. This means it only has one responsibility. If someone asks you to explain what your module does and you use the words “or/and/also…” then it most likely means your module violates the single responsibility principle. Keep in mind, there is no universal definition of what a module does, it’s up to you to determine the granularity of it.
“Do one thing and do it well“
— Unix philosophy
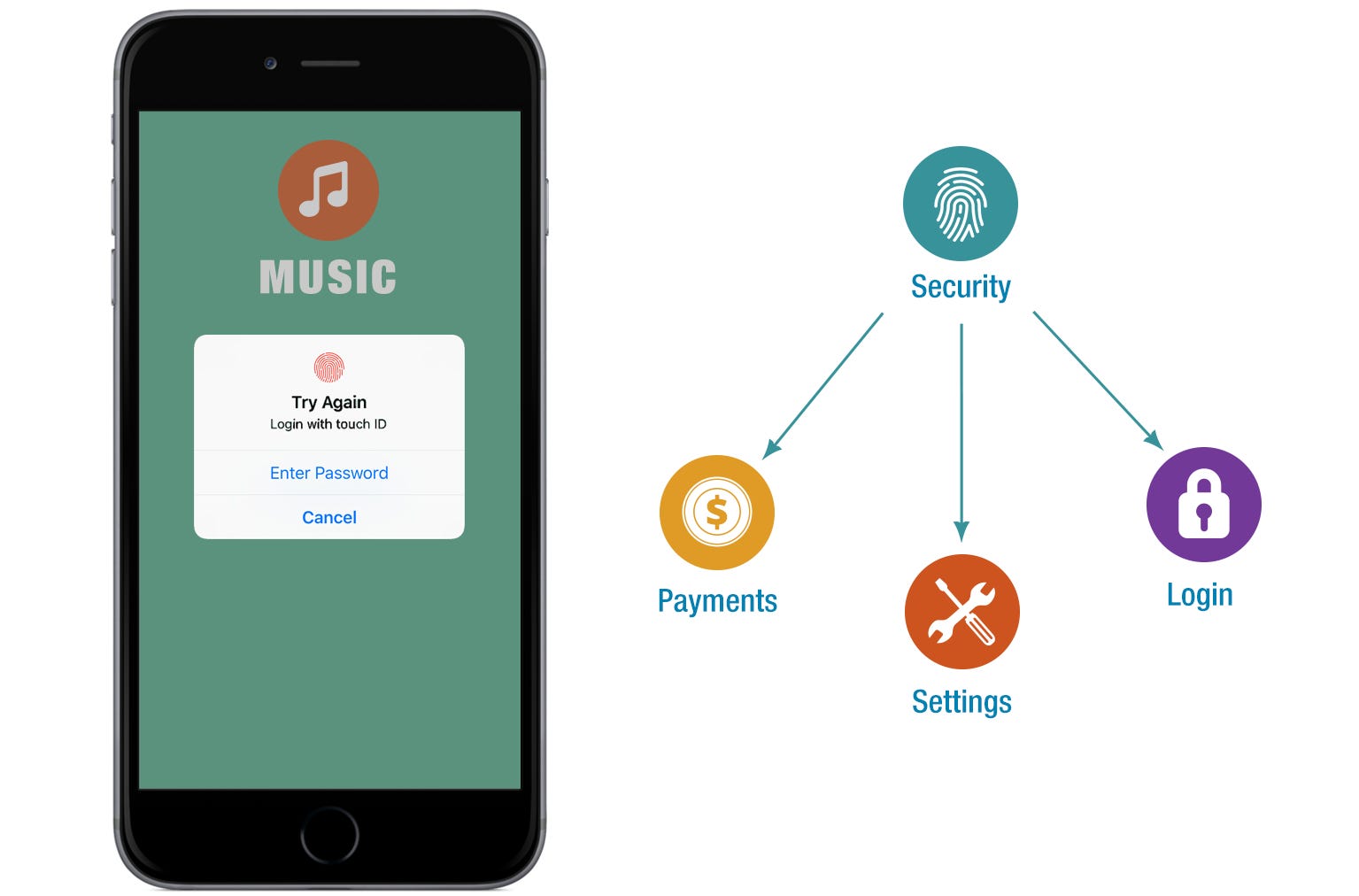
I compose my modules based on what they provide to the user. For example, if I want to create a mobile application using React-Native which provides the ability to use the device’s fingerprint scanner, I would pack together all the methods related to the fingerprint scanner. This includes the in-app popups requesting to touch the sensor for all platforms. Whether you use the fingerprint scanner to login, authorize a payment or as part of the settings section of your app, everything related to the scanner comes from a single place. This is your module.
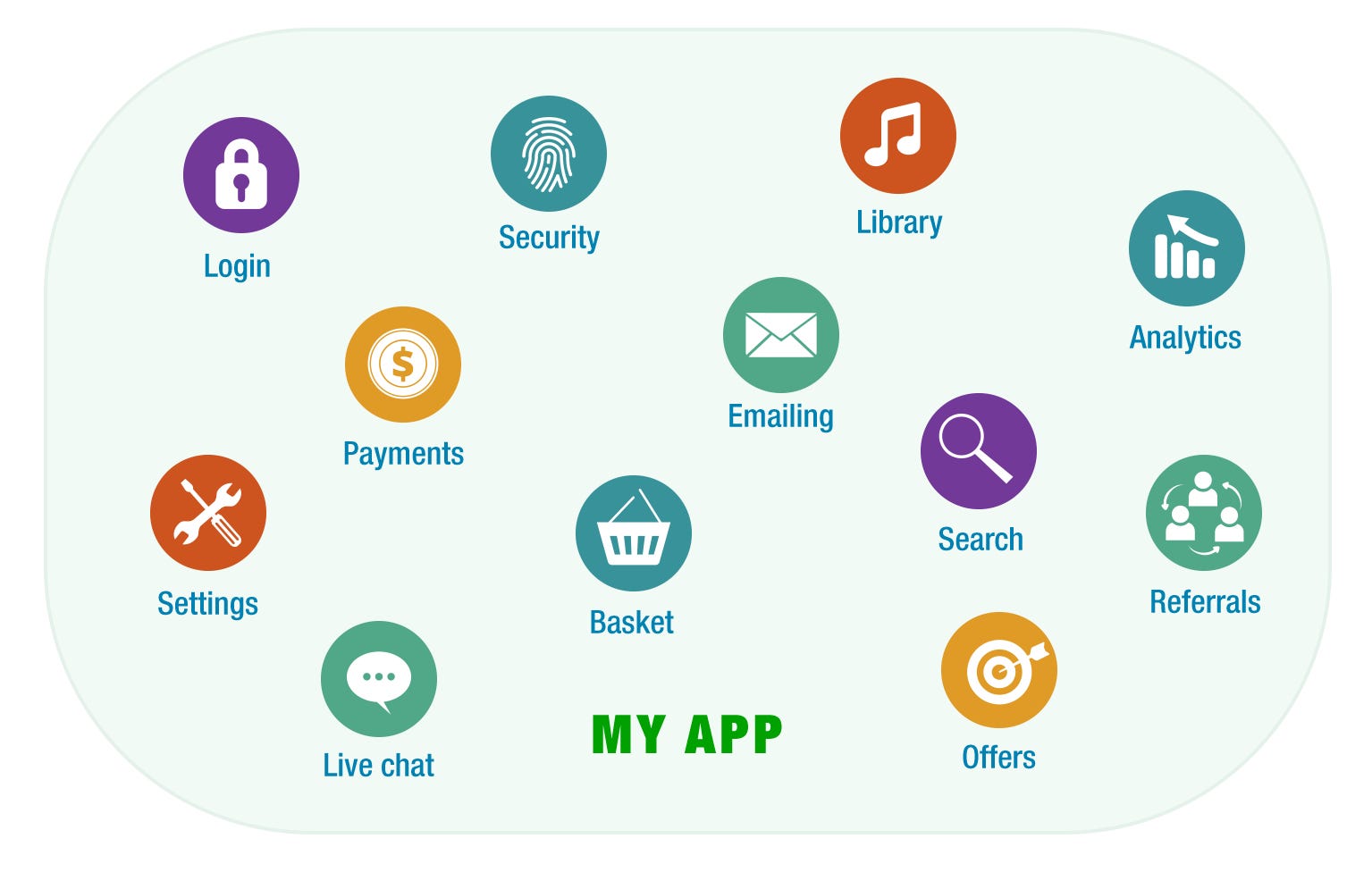
Why you should follow this structure?
Code organized by kind is certainly one of the most popular ways for javascript developers to structure their applications, putting files in buckets based on what they are, without considering the different relationships between the files. Categorizing files based on what they represent is an easy way of partitioning your project and has became a popular practice with developers who use patterns such as MVC. In my experience, that’s okay when you work on small applications, but it can have a tremendous effect on the team’s velocity as the application grows.
When you work on a large project, it can be a difficult to identity to origin of an issue. As a developer, you might spend valuable time digging through thousands of lines of code until you understand all the relationships. Organizing your code by modules means you start thinking around a concept where you break down your code into related pieces and provide a public interface to use your module. It helps maximize code sharing and reusability in different sections of your application and even on other projects.
Another important attribute of a module-based structure is the ability to replace one by another, as long as both modules meet the same requirements. In a world where everything moves fast and new features replace old ones in no time, breaking your code by modules will give you the freedom to build multiple versions of them to facilitate A/B testing and fully replace old ones when your team is satisfied with the result.

Applying this concept to your React applications
Creating a module means you will group a set of related components, methods and assets together, providing a public interface to be used by other modules. Just like you would create a node module.
Let’s create a module called security for a React-Native application. This module will allow a user to use the fingerprint sensor or facial recognition on their device and fallback to a pin number whenever there is no sensor available. Here is how our module is structured.
/security
/__tests__
/Authenticate.js
/sensor.js
/user-preferences.js
/PinPopup
/__tests__
/index.js
/index.js
/lock-icon.png
/SensorPopup
/__tests__
/index.js
/failed-icon.png
/fingerprint-icon.png
/index.js
/success-icon.png
/Authenticate.js
/index.js
/sensor.js
/user-preferences.jsWhen you render the Authenticate component, the user is prompted to authenticate himself. This component consumes methods from sensor.js which defines methods for enabling/disabling the sensor and for verifying its availability. If the sensor is available and set up, the Authenticate component takes care of rendering the SensorPopup component which uses the sensor for authentication. Otherwise, it will render the PinPopup component which will verify the user’s pin against what has been previously saved in the storage, using methods from user-preferences.js. Once one of the popups is done validating the user’s credentials, the Authenticate component receives the information and triggers either onSuccess or onFail methods, followed by onComplete.
Our module is now ready to be used within different sections of our application.
render() {
return (
<View>
{this.state.requestAuthentication &&
<Authenticate
onSuccess={()=> console.log('Success!')}
onFail={()=> console.log('Failed!')}
onComplete={()=> this.setState({ requestAuthentication: false })}
/>
}
</View>
);
}The module will be used by other modules to authorize an access or an action. For example, it can be used by the Login module to log the user in, by the Payments module to authorize a payment, and by the Settings module to enable or disable the sensor from the app preferences. It provides a public interface, meaning it only exports a few methods to make accessible to the outside world, the Authentication component, the sensor methods, as well as the user-preferences methods. The popup components are not exported as you are not supposed to use them directly.
The modular pattern can also be applied within modules themselves to structure files around what they do rather than what they are. A few years ago, I demonstrated How to better organize your React applications, exposing the benefits of bringing together related pieces of code. This structure pattern works for React and can certainly be applied to many javascript projects. Nowadays, I structure my modules using an approach similar to the suggested Component folder pattern by Donavon West assembling related components together and breaking them down when they become too big. It’s also important to limit nested folders to 3-4 levels to avoid complexity. I define non-component files, such as api call services or redux files, at the top level of my modules outside any component, or I create modules only taking care of the business logic.
Advanced level: the multi-package repository
You might come to a point where you’ll have created a module you want to reuse in other projects. In order to do this, you create a new git repository where your module will live, you publish it to a npm repository, and have your project consuming it. As the number of modules grows, so does the number of git repositories and you may end-up having more difficulties maintaining and managing them all. A single change will have you modifying several repositories and creating multiple pull requests, each of them requiring to be reviewed and approved. You will most likely have trouble syncing modules or having successful CI build and you’ll end up spending a considerable amount of time to finally get your changes. If I sound excessively opinionated it’s because I’ve experienced those problems in my current role. Sharing code efficiently at scale is hard and we needed a solution to improve our velocity. After some research, we decided to introduce a single multi-package javascript repository.
Juggling a multi-module project over multiple repos is like trying to teach a newborn baby how to ride a bike.
— Sebastien McKenzie — creator of Babel, Yarn, Facebook Engineer
This means that you will end up with multiple projects within the same git repository. Many companies such as Google, Facebook or AirBnB use the single repository strategy for their projects. The often called “mono-repo” helps you coordinate changes across projects and libraries to increase your velocity and continuous modernization. Code reviews become faster as you only need a single pull request to modify multiple projects — as an atomic unit. Another great feature is share the same configuration files for all your projects, whether you use Jest, Eslint or TypeScript, which can be defined at the root level of your repository.
There are some libraries which can help you manage your repository. I personally use Lerna — it allows you to turn your codebase into packages, which can then be published to npm independently. It also provides powerful tools for versioning and running cross-package commands.
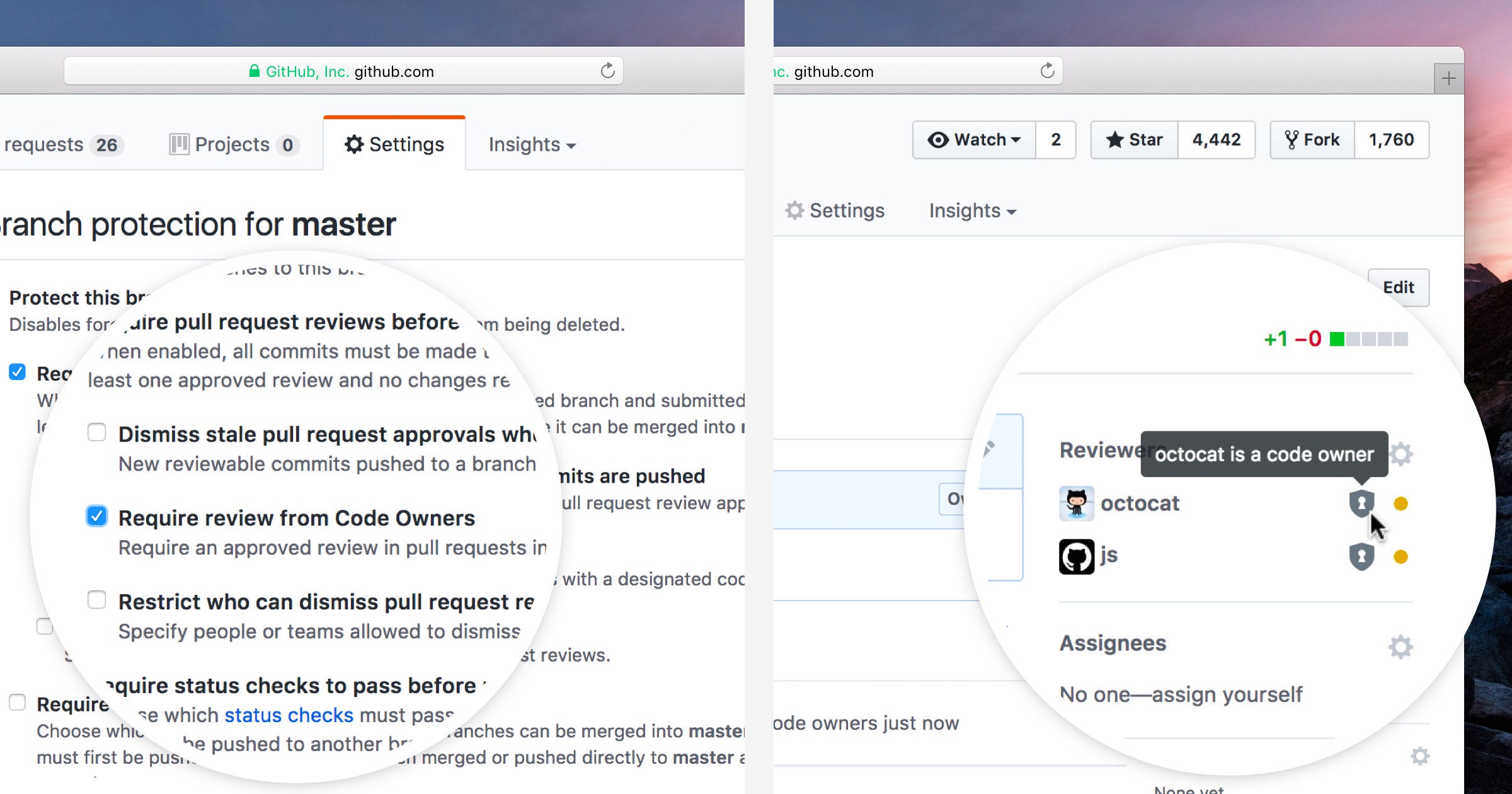
Another great tool you might want to consider is the GitHub’s Code Owners feature. With a multi-package repository it’s not always clear who owns which package and Code Owners allows you to assign ownership to specific folders. This feature requires code owners to review pull requests changing their owned code. This ensures code quality and adds an extra layer of security.
Here is a final look at how you can have multiple React-Native applications reusing the same modules in a single repository managed by Lerna. We have 3 different mobile applications, which define their own navigation, and the shared modules that they used within the same repository. And if you ever feel like your security module is amazing you can publish it to npm.
/.github
/CODEOWNERS
/node_modules
/packages
/AdminApp
/CustomersApp
/SellersApp <--- those are the app containers with navigation
/analytics
/basket
/emailing
/library
/live-chat
/login
/offers
/payments
/referrals
/search
/security
/settings
/.eslintrc <--- same lint rules
/jest.config.js <--- same jest config
/lerna.json
/package.jsonWrapping up
Now that you’ve decided to introduce squads and tribes in your company, I hope you will also be able to negotiate some time with your manager to reorganize your projects using this modular structure.
Thinking large scale is not easy, you can’t really assume the future, how many developers will be working on your app and how to prevent them from over-engineering when it grows. A modular pattern can help you scale your application without the need to anticipate future features and evolutions that will be introduced next.
Source: https://medium.com/@alexmngn/why-react-developers-should-modularize-their-applications-d26d381854c1